About Our Services and Procedures Offered at Victorian Cardiac Care
Coronary Angiography
This procedure involves the use of X-ray imaging to view the heart's blood vessels, identifying blockages or abnormalities. It's often performed to diagnose various heart conditions, especially those related to coronary artery disease. A contrast dye is injected into the coronary arteries, making them visible on the X-rays.

Coronary Angiography
CTO (Chronic Total Occlusion) Procedures
These are advanced interventions aimed at treating completely blocked coronary arteries, a condition known as chronic total occlusion. These procedures often involve sophisticated techniques to navigate or cross the blockage and restore blood flow. Success in CTO procedures can significantly improve symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath in patients with heart disease.
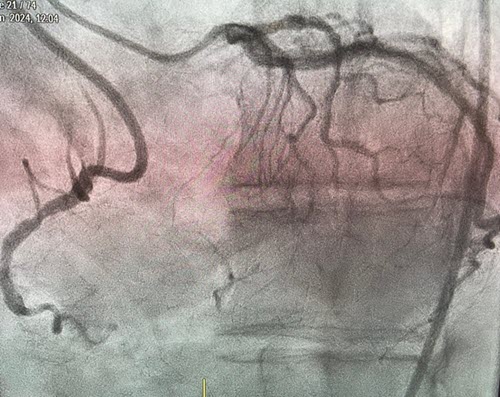
CTO (Chronic Total Occlusion)
Coronary Angioplasty
This is a treatment method for opening narrowed or blocked coronary arteries, usually caused by plaque buildup. A balloon catheter is inserted into the affected artery and inflated to compress the plaque and widen the artery. Often, this procedure is combined with the placement of a stent to help keep the artery open.
Coronary Artery Stenting
In this procedure, a small mesh tube called a stent is permanently placed in the narrowed or blocked coronary artery. The stent helps prevent the artery from narrowing again in the future. Stenting is often performed in conjunction with angioplasty to ensure the artery remains open after the initial procedure.
Left Main Interventions
LM interventions tend to have comparable clinical outcomes with
CABG in the presence of mild and moderate anatomic complexity. Technical
expertise and imaging utilization are important components in achieving optimal
long-term clinical outcomes.

Left Main Intervention - Before
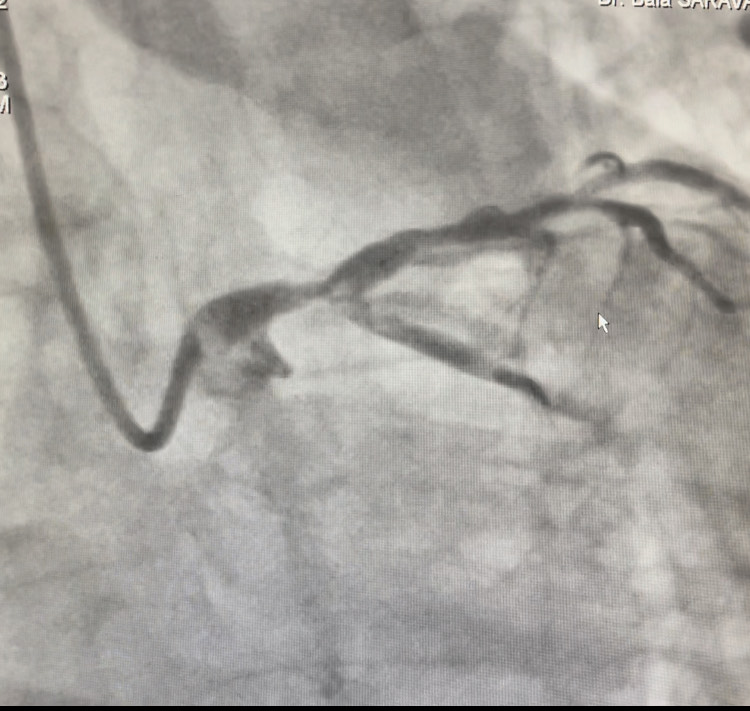
Left Main Intervention - After
Rotablation
Rotablation is a specialized procedure to remove hardened plaque from coronary arteries. It involves a tiny, diamond-coated drill that rotates at high speeds to grind away plaque. This procedure is used particularly for calcified blockages that are hard to treat with standard angioplasty.
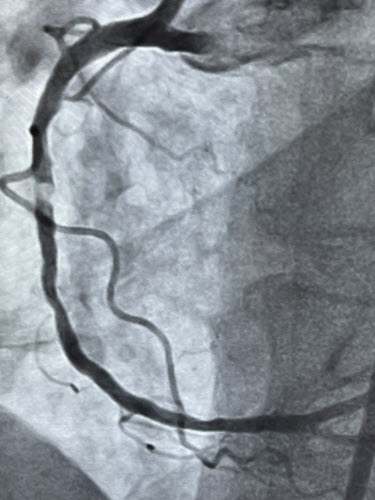
Rotablation
Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP)
Intra-Aortic
Balloon Pump (IABP) or intra-aortic counterpulsation device
The
balloon is inflated during diastole to increase coronary perfusion and then
deflated during systole to decrease afterload.
This
aims to improve myocardial oxygenation, increase cardiac output and organ
perfusion with a reduction in left ventricular workload.
Holter Monitoring
Holter Monitoring is a diagnostic tool that continuously records the heart's rhythm, usually over a 24-48 hour period. It's used to detect heart rhythm abnormalities that might not be found during a standard ECG test. Patients wear a small, portable device that monitors their heart as they go about their daily activities.

Holter Monitoring
Echocardiogram
This is a non-invasive ultrasound test that creates images of the heart to assess its structure and function. It helps in diagnosing various heart conditions, such as valve diseases, heart failure, and congenital heart defects. Echocardiograms can also measure the heart's ejection fraction, which indicates how well the heart is pumping blood.
Stress Echocardiogram
This test combines an echocardiogram with a stress test to evaluate the heart's function under stress. It's often performed by having the patient exercise on a treadmill or bike, or by administering medication that simulates exercise. The stress echocardiogram helps diagnose coronary artery disease and assess the severity of heart conditions.

Stress Echocardiogram
Consultations
Consultations in a cardiac context involve in-depth discussions between patients and their healthcare providers about heart health, symptoms, and treatment options. They are essential for diagnosing heart conditions, planning treatment strategies, and providing patient education. These sessions also allow patients to ask questions and express concerns about their heart health.

Dr Bala in his consulting room
ABPM
ABPM is the use of a portable wearable device that takes repeated blood pressure readings every 15–60 minutes over 24 hours as the patient details specific periods of activities – such as sleep, meals or exercise – in a diary. Interpretation includes analysis of the daytime readings, night-time readings and presence or absence of nocturnal dipping. It is the reference standard for the diagnosis of hypertension, with elevated readings associated with cardiovascular disease independent of clinic measurements.

ABPM